The Morgan Library in New York recently hosted a conversation between Maria Popova and Sophie Blackall, “Children’s Books as Philosophy for Living,” and the recording is available on their website. (The Morgan Library, incidentally, is where I learned that E.B. White, author of The Trumpet of the Swan and Charlotte’s Web, is the same E.B. White as The Elements of Style by Strunk & White. I cannot now find a listing for that exhibit on the Morgan website, but I am 99% sure that’s where I saw his manuscripts, journals, and letters and made the connection. Anyway…)

Popova and Blackall discussed, among other things, A.A. Milne’s Winnie-the-Pooh, Antoine de Saint-Exupery’s The Little Prince, and Beatrix Potter’s Peter Rabbit, as well as her scientific drawings. In the photo above, they’re wearing scarves, like the little prince’s iconic scarf, which resembles Piglet’s ears. (Sophie: “It was Piglet’s ears that made me want to be an illustrator….how to convey emotion in a couple of lines…” Maria: “Isn’t it amazing how these influences and ideas permeate the psyche, often without our awareness, and kind of lodge themselves in there and become these quiet building blocks of what we create, often without us knowing that we’re creating out of these borrowed pieces?”)
Here are a few more quotes from the talk, but if you are interested in children and children’s literature, it’s worth an hour of your time to watch the whole thing. Sophie brought a list (see photo below) to keep their conversation on track.

“I don’t believe in moralizing children, but I do believe that morality is a branch of the imagination, just like creativity and curiosity, and if the imagination is rooted in kindness, then morality stands a pretty good chance.” -Maria Popova
“Children’s books to me, the ones that endure, can be read both when you’re a child and when you’re a grownup. And as a reader of any book you bring so much of yourself to it.” -Maria Popova
“Fantasy mystifies in order to reveal some deeper truth, and fundamentalism mystifies in order to conceal.” -Maria Popova
“And that’s what story gives children, that agency to imagine themselves as characters in a different story, of telling different stories, of unbelieving the main story, the mainstream story.” -Maria Popova
“I want to foster a curiosity in children, so that they will feel confident that they can read any book that they might want to pick up….If a child is encouraged to be curious, I believe that they will continue to read and they will become a more empathetic human being and I think we need that more than ever.” -Sophie Blackall
“We are trying to arm [children] with everything we know to be true, and that is what we are trying to put into the books that we give to children.” -Sophie Blackall
Toward the end of the conversation, they mention author Katherine Rundell’s work, Why You Should Read Children’s Books, Even Though You Are So Old and Wise. You can read an excerpt here: Why Adults Should Read Children’s Books. Rundell quotes Marina Warner: “Fairy tales…evoke every kind of violence, injustice and mischance, but in order to declare it need not continue.” [emphasis added] Rundell continues, “Fairy tales conjure fear in order to tell us that we need not be so afraid. Angela Carter saw the godmother as shorthand for what she calls “heroic optimism”. Hope, in fairy tales, is sharper than teeth.” Children’s books satisfy the desire for justice and foster a sense of wonder and awe. And don’t we all, no matter how old, want justice and wonder?

 Enter What If We Get It Right?: Visions of Climate Futures by Ayana Elizabeth Johnson and a whole host of experts she interviews. The central takeaway is that we have the ideas, tools, and technology we need to tackle the climate crisis right now; what we’re lacking is the political will to make these changes with all necessary speed. Even so, a book so stuffed with brilliant ideas and solutions and energy is motivating; as Paola Antonelli, MoMA’s senior curator for architecture and design and its founding director of research and development, said, “Hope is a propellant.”
Enter What If We Get It Right?: Visions of Climate Futures by Ayana Elizabeth Johnson and a whole host of experts she interviews. The central takeaway is that we have the ideas, tools, and technology we need to tackle the climate crisis right now; what we’re lacking is the political will to make these changes with all necessary speed. Even so, a book so stuffed with brilliant ideas and solutions and energy is motivating; as Paola Antonelli, MoMA’s senior curator for architecture and design and its founding director of research and development, said, “Hope is a propellant.”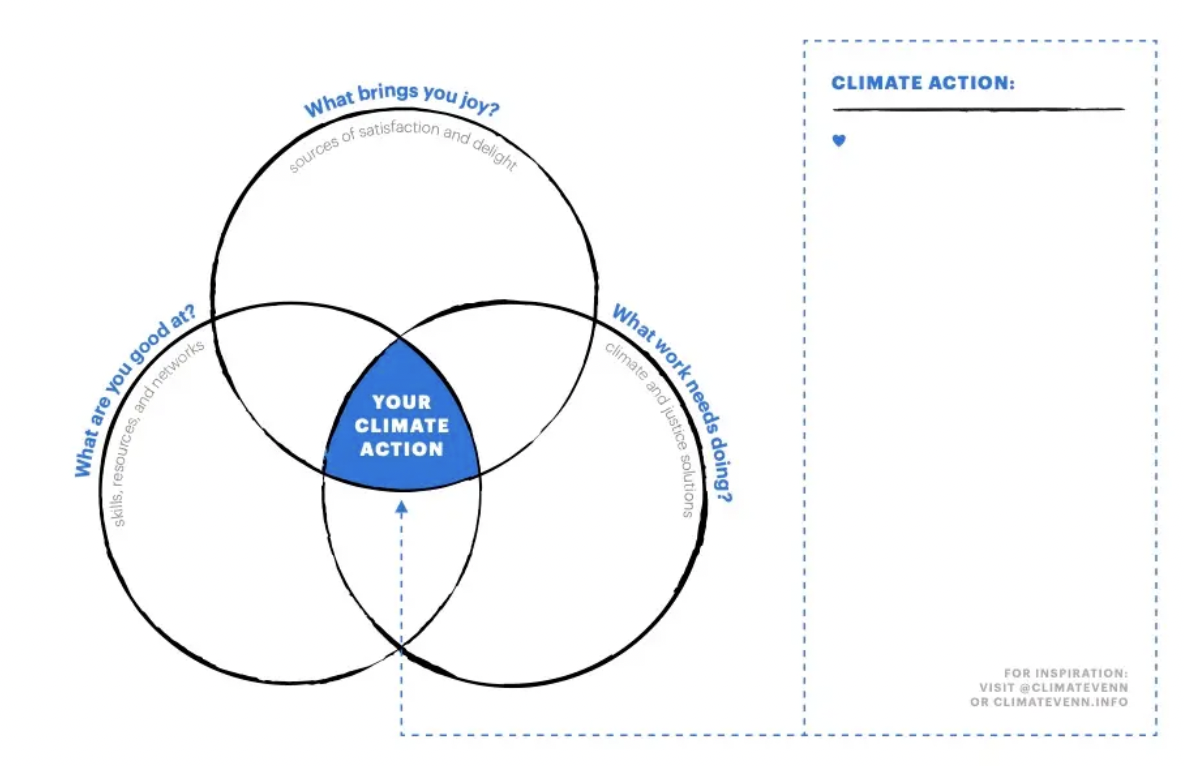
 I wish I remember where I heard about Once Upon A Time We Ate Animals: The Future of Food by Roanne Van Voorst, but I requested it mainly based on the intriguing title (I love speculative fiction – and nonfiction). Van Voorst is a “futures anthropologist” and her premise for this book is that we are currently in the middle of a shift from “carnism” (eating meat and animal products) toward vegetarianism and veganism. The book is nonfiction, but spliced in are short fiction pieces set in the future, looking back on a past in which (many) humans ate animals. Whether you’re an omnivore, vegetarian, vegan, or other, this is a fascinating book, and will make you think differently about the way you eat – no matter which way that is currently.
I wish I remember where I heard about Once Upon A Time We Ate Animals: The Future of Food by Roanne Van Voorst, but I requested it mainly based on the intriguing title (I love speculative fiction – and nonfiction). Van Voorst is a “futures anthropologist” and her premise for this book is that we are currently in the middle of a shift from “carnism” (eating meat and animal products) toward vegetarianism and veganism. The book is nonfiction, but spliced in are short fiction pieces set in the future, looking back on a past in which (many) humans ate animals. Whether you’re an omnivore, vegetarian, vegan, or other, this is a fascinating book, and will make you think differently about the way you eat – no matter which way that is currently. Animal, Vegetable, Miracle: A Year of Food Life was published in 2007, but I didn’t get around to reading it until 2022. It is a year in the life of the Kingsolver family at their homestead, where they’ve committed to eating only what they can grow or source locally for one year. There are many good reasons to eat local, from climate to animal welfare to supporting the community you live in, though you don’t need to devote your life to growing all your own food and raising chickens (unless you want to!). There are farmers’ markets and CSA shares and local groceries in a lot of places – other places, unfortunately, are food deserts, and there’s plenty of advocacy to be done there – and when you eat foods that are in season, they taste better too. (Animal, Vegetable, Miracle also includes recipes.)
Animal, Vegetable, Miracle: A Year of Food Life was published in 2007, but I didn’t get around to reading it until 2022. It is a year in the life of the Kingsolver family at their homestead, where they’ve committed to eating only what they can grow or source locally for one year. There are many good reasons to eat local, from climate to animal welfare to supporting the community you live in, though you don’t need to devote your life to growing all your own food and raising chickens (unless you want to!). There are farmers’ markets and CSA shares and local groceries in a lot of places – other places, unfortunately, are food deserts, and there’s plenty of advocacy to be done there – and when you eat foods that are in season, they taste better too. (Animal, Vegetable, Miracle also includes recipes.) Ultra-Processed People: The Science Behind Food That Isn’t Food by Chris van Tulleken draws the reader’s attention to how much of the “food” we eat isn’t really food at all (as the subtitle indicates). Van Tulleken introduces the NOVA framework for classifying foods, from (1) unprocessed/minimally processed to (2) processed culinary ingredients (e.g. butter) to (3) processed food (e.g. canned beans) to (4) ultra-processed food (e.g. Coke, Doritos). One of the shocking pieces of information in this book was that the FDA does not regulate foods, or the ingredients that go into foods, anywhere near as much as you might imagine; there are giant loopholes for additives; companies can just say that various chemicals are safe without having any real scientific evidence to back that up.
Ultra-Processed People: The Science Behind Food That Isn’t Food by Chris van Tulleken draws the reader’s attention to how much of the “food” we eat isn’t really food at all (as the subtitle indicates). Van Tulleken introduces the NOVA framework for classifying foods, from (1) unprocessed/minimally processed to (2) processed culinary ingredients (e.g. butter) to (3) processed food (e.g. canned beans) to (4) ultra-processed food (e.g. Coke, Doritos). One of the shocking pieces of information in this book was that the FDA does not regulate foods, or the ingredients that go into foods, anywhere near as much as you might imagine; there are giant loopholes for additives; companies can just say that various chemicals are safe without having any real scientific evidence to back that up.







